Electric range-extenders have been a topic of discussion in the automotive industry for nearly three decades, offering a potential solution to reduce reliance on traditional petrol and diesel powertrains. With the introduction of new eRE and eRE+ powertrain options from ZF Friedrichshafen in 2026, the future of range-extender technology looks promising.
The longevity of range-extenders is evident, with Citroën pioneering models like the Saxo, Xsara, and Berlingo in the 1990s. Other manufacturers have also explored this technology, with notable examples such as the Chevrolet Volt and the Mazda MX-30 R-EV. ZF, a leading automotive tier one supplier, is making significant investments in range-extender technology to streamline its integration into production vehicles.
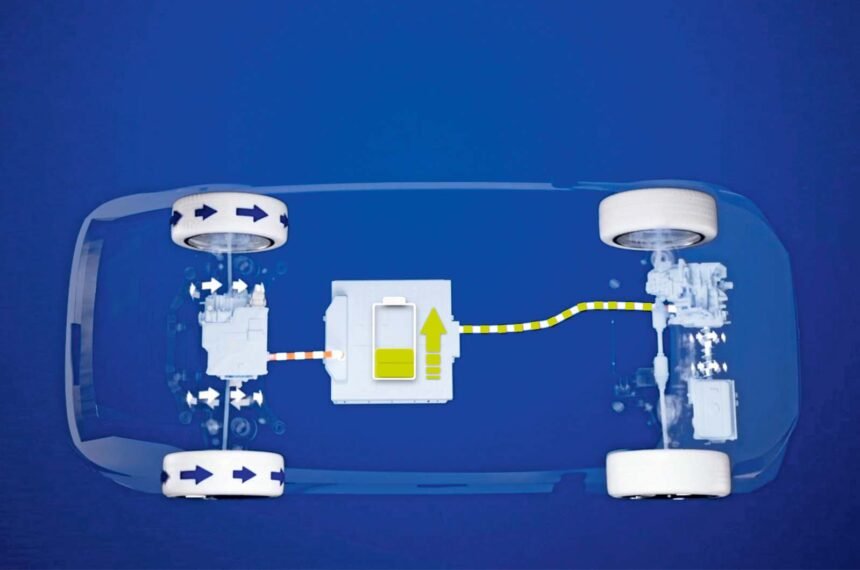
Range-extenders function as electric vehicles with a smaller battery and a generator to supplement power when needed. Unlike traditional hybrid systems, where the engine and electric motor can drive the wheels independently, a range-extender utilizes a series hybrid configuration. In this setup, the combustion engine powers a generator, which charges the battery that, in turn, powers an electric motor driving the wheels.
The ZF eRE and eRE+ powertrains offer a versatile solution, with the eRE+ adding a planetary gearset, bi-directional clutch, and differential to enable four-wheel drive capability. This innovative design allows for the motor-generator to drive the front wheels while the main motor powers the rear wheels, offering enhanced performance and flexibility on the road.
By focusing on modular integration and advanced engineering, ZF is at the forefront of range-extender technology, catering to the evolving needs of the automotive industry. With a growing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles, range-extenders could play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable transportation.