Challenges Faced by Tesla in Optimus Production
Recent reports from China’s supply chain suggest that Tesla may be pausing production of its humanoid robot, Optimus. According to TrendForce, Tesla is encountering two major challenges in the production process: limited battery life and difficulties with hardware-software integration. Improvements in motion planning and energy optimization through AI could potentially address battery performance issues, but fundamental bottlenecks remain in the efficiency of core hardware components like joint motors and transmission systems.
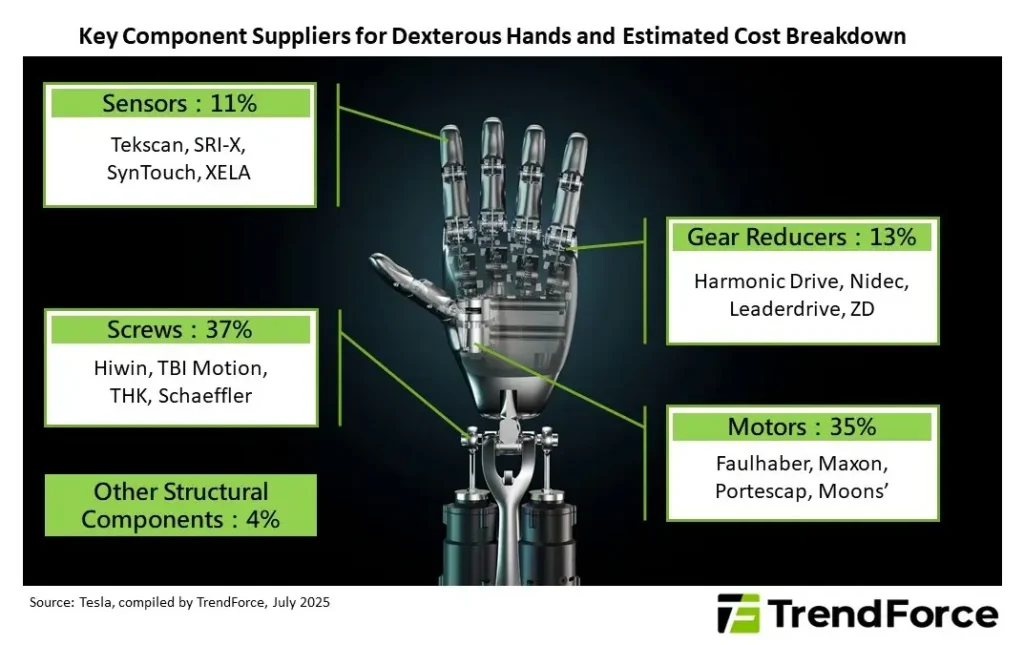
Furthermore, reports indicate that Optimus’ dexterous hand is facing payload issues due to the complex integration of precision mechanics, miniature actuators, and AI-driven control systems. These challenges require sophisticated human behavior simulation and longer development cycles.
Optimus Program and Future Considerations
In its April report on humanoid robots, TrendForce highlighted the importance of finalizing product specifications by mid-year to avoid jeopardizing mass production timelines. If Tesla intends to continue the Optimus program, it will need to refine its technology, explore new suppliers for dexterous hand modules, and potentially consider adjusting the robot’s design or application. This could involve focusing on household tasks or simplifying the design complexity to enhance practical functionality.
While the reported production pause has attracted market attention, it may present an opportunity for companies to reassess design choices and accelerate real-world implementation. The gap between design logic and real-world conditions poses a challenge for manufacturers, including Tesla, despite its funding, data, and hardware integration advantages.
Impact on Taiwanese Suppliers and Industry
The impact of the production halt on Taiwanese suppliers is expected to be minimal. Tesla’s humanoid robot development has primarily relied on in-house components sourced from US-based solutions, limiting Taiwanese involvement. Moreover, Optimus and similar robots are still in the development and testing phases, distant from mass production or commercial-scale development.
Even if Tesla sticks to its production targets of 5,000 units in 2025 and 50,000 units in 2026, initial production volumes will be limited, offering modest contributions to supplier revenue. Therefore, the reported production pause is unlikely to significantly affect Taiwan’s component supply chain, and suppliers may not need to make immediate adjustments to resource allocation or production strategies.